
UV-curable inkjet printing inks dominate the packaging industry, especially for food packaging. The packaging market’s overall growth is projected to reach a CAGR of over 5% through 2024, a trend leading to the formulation of more versatile UV and other inks capable of printing on various product surfaces, shapes, and packaging types.
Advantages of UV Printing Inks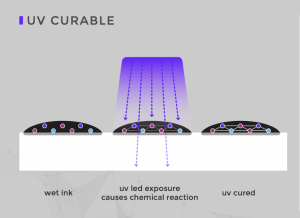
- Excellent adhesion
- No primer coating needed
- High-quality finishes
- Different printing effects
- Lightfast
- High durability
- Fast drying (curing)
- Environmental friendly, no VOCs
Ultraviolet systems use two different lighting methods for curing inks: mercury arc lamps and LED lamps. The future of curing UV inks with mercury arc lamps is uncertain because of the tightening regulations governing the use of mercury.
Kao Collins Inkjet Inks with Low or No VOCs
Download
While there are regulatory exemptions for some industrial uses of mercury arc lamps, printers remain in limbo regarding the future of those exemptions. Even though mercury arc lamps contain low amounts of mercury, regulators may ban all uses of mercury-containing materials in the future.
Industrial printers should begin looking for alternative printing systems and UV inks that can replace aging and environmentally unfriendly mercury-based systems.
Three UV ink alternatives
Why Printers are Moving Away from Mercury-arc Curing
Concerns over the danger of mercury poisoning originated from the diagnosis of a wide-spread disease affecting the central nervous system in residents within communities surrounding Minamata Bay, Japan, in 1956. Investigators found high levels of mercury in food fish. The source of the contamination came from industrial discharge into the bay. Another concerning incident during the 1970s involved Iraq citizens who were poisoned after consuming feed grain treated with a mercury-based fungicide.
International negotiations started in 2001 on the foundation of the Minamata Convention on Mercury. The agreement came into effect in 2017.
What does the Minamata Convention on Mercury cover?
- Taking steps to eliminate new sources of mercury
- Reducing the use, trade, and emissions of the element
- Regulating the disposal of equipment containing mercury
The reluctance of industrial printers to switch from mercury-based curing lamps is understandable because of how much they have invested in their enterprise systems. However, factoring in certain externalities changes the equation when it comes to the ROI of continuing to use mercury lamps.
Ongoing Mercury Lamp Cost Factors
- Cost of bulbs – With the restricted trade of mercury, the price for bulbs will only increase.
- Environmental cost – Countries party to the treaty have implemented strict recycling regulations that only drive up the cost of disposing of spent bulbs.
- Health cost – Accidental breakage exposes employees to mercury vapors
3 Options for Printing Inks Without Mercury-arc Lamps
Here’s a closer look at the options with advantages and disadvantages.
1. LED-curable Inks
See Our LED Curable Inks
Get Started
The primary alternative for mercury-lamp systems is LED. Attention has often focused on the higher cost of LED lighting systems and bulbs. The sticker shock can be misleading when compared to other advantages of LED systems for inkjet curing.
Advantages of LED Curing
- Lower temperatures: The LEDs have minimal heat transfer, and infrared (IR) radiation is emitted through the back of the module. This offers more options for printing on heat-sensitive substrates, such as thin packaging films.
- Lower-voltage and wattage: These systems are simpler and safer. Also, more of the electricity is converted into light rather than heat.
Environmentally friendly: No dangerous UVC radiation or ozone, which requires ventilation, is created. The bulbs do not contain heavy metals. The bulbs consume significantly less electricity. - Less downtime: Unlike mercury lamps, LEDs are called instant-on/instant-off. Cooling down before restarting is not necessary. That keeps production running.
- Longer life: LED bulbs have a longer life span and a consistent light spectrum over the life cycle.
Disadvantages of LED Curing
- Limited spectrum: LEDs emit a narrower spectrum of UV light. This limits the photoinitiators that can be used in the ink.
- Higher cost of ink: LED’s limited options for photoinitiators increases the cost of consumables.
- Less durability: For some printing applications, LED inks may have less scratch resistance. Chemistry advancements continue to improve LED ink durability.
How do Light-curing Inkjet Systems Compare Side-by-Side
Here’s a quick look at the two UV-curable systems.
| UV-curable Inkjet Systems: Mercury vs. LED | ||
|---|---|---|
| UV Curable – Mercury Bulbs | UV Curable – LED Bulbs | |
| Light Spectrum | Broad | Narrow |
| Heat generated | High | Low |
| Emissions |
|
None |
| Substrates | Limited because of high heat output that can damage fragile materials causing distortion or melting. | Less heat output makes it more suitable for thin films and other heat-sensitive substrates. |
| Ink cost | Lower cost because there is a broader range of photoinitiators that react to the light spectrum. | Higher cost because fewer photoinitiator options compatible with the light spectrum and complexity of the formulations. |
| Ink options | More | Fewer |
| Adhesion | Strong adhesion without pretreatment | Strong adhesion without pretreatment |
| Bulb lifespan | Approximately 1,000 hours. The output decreases as the bulb ages. | Approximately 10,000-15,00 hours. Output remains consistent over the life of the bulb. |
| Operation | The bulb requires a warm-up and cool-down period. | Instant-on/off |
| Energy consumption | High | 30-50% lower than Mercury |
2. Using Specialty Water-Based Pigment Ink
 Everyone “knows” water on glass or plastic will not stick. With ink innovations in recent years, that is no longer true. Traditional water-based inks can’t be used on non-porous substrates without a primer, which increases production cost. New water-based formulations using nanotechnology and new resin chemistry make water-based inkjet inks a viable alternative for printing thin films, flexible packaging, and other non-porous substrates.
Everyone “knows” water on glass or plastic will not stick. With ink innovations in recent years, that is no longer true. Traditional water-based inks can’t be used on non-porous substrates without a primer, which increases production cost. New water-based formulations using nanotechnology and new resin chemistry make water-based inkjet inks a viable alternative for printing thin films, flexible packaging, and other non-porous substrates.
See Our Water-Based LunaJet Inks
Get Started
Advantages of Water-Based Inks
- No heat or curing: Specially formulated aqueous inks don’t require external methods for drying or curing.
- No primer: The formulation of the water-based pigment ink makes it unnecessary for any primer or other pretreatment of substrates.
- Lower carbon footprint: These environmentally friendly inks don’t emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Because no external curing or ventilation is needed, there are no elevated utility costs.
Disadvantages of Water-Based Inks
- Speed: Production speeds may not match curable inks.
- Cost: Specialty water-based pigments may be more costly, however, they don’t require curing systems.
Specialty Electron Beam (EB) Curable Ink
 Rather than light waves, electron beam systems use electrons generated in a vacuum chamber. The electron molecules react with monomers and oligomers in the fluid to create a solidly-cured polymer.
Rather than light waves, electron beam systems use electrons generated in a vacuum chamber. The electron molecules react with monomers and oligomers in the fluid to create a solidly-cured polymer.
Advantages of EB Inks
- No photoinitiators: Without photoinitiator catalysts, the inks reduce migration risk when printing food, medical, and pharmaceutical products.
Substrate penetration: The electron-beam energy penetrates the ink to reach the substrate, producing a better cure with increased adhesion. Also, thicker ink coatings can be applied for special printing effects or braille coding. - More substrates: The ink colors and substrate material do not affect the absorption and penetration of electron-beam energy, expanding the range of materials using a single curing technology. The electron-beam energy binds the ink regardless of the substrate reflectivity.
- Environmentally friendly: These inks don’t release volatile organic compounds.
Disadvantages of EB Inks
- Cost: The price of EB curing equipment, maintenance, and ink are higher than mercury-arc systems. However, typical EB equipment costs are dropping.
- Complexity: EB curing systems are more complex than other curing systems, posing a learning curve for operators. For example, in addition to the electron system, nitrogen is often used to displace oxygen for better curing.
How Market Dynamics are Accelerating the Shift Away from Mercury
Regardless of whether exemptions for mercury-based systems for inkjet printing continue, other market factors are also influencing the adoption of alternative printing systems.
Heatless Curing Needed for Popular Substrates
 The increasing use of flexible packaging and thinner films requires curing ink without heat, which could damage the substrate. While heat is a concern for mercury systems, the three alternatives to curing inks with mercury lamps that are listed above all produce little or no heat.
The increasing use of flexible packaging and thinner films requires curing ink without heat, which could damage the substrate. While heat is a concern for mercury systems, the three alternatives to curing inks with mercury lamps that are listed above all produce little or no heat.
Consumers prefer flexible resealable packaging, and, in a post-Covid world, consumers are looking for more single-serve packaging. With this in mind, the demand for heatless curing will only grow, removing the appeal of mercury curing systems and adding to the opportunity cost of using them.
Prioritizing Energy Costs and Sustainability
UV-curable systems using mercury lamps consume the most energy. The alternative options, especially LED and water-based inks, reduce energy costs and support sustainability efforts.
More and more brands recognize the need and value of adopting more sustainable production methods. They hear consumers demanding more environmental responsibility from companies. Also, tighter regulations throughout the supply chain make incorporating eco-friendly solutions a higher priority.
Kao Collins experts can discuss with your printing goals to identify alternatives for UV-curing with mercury bulbs. Contact us about inks and options.






