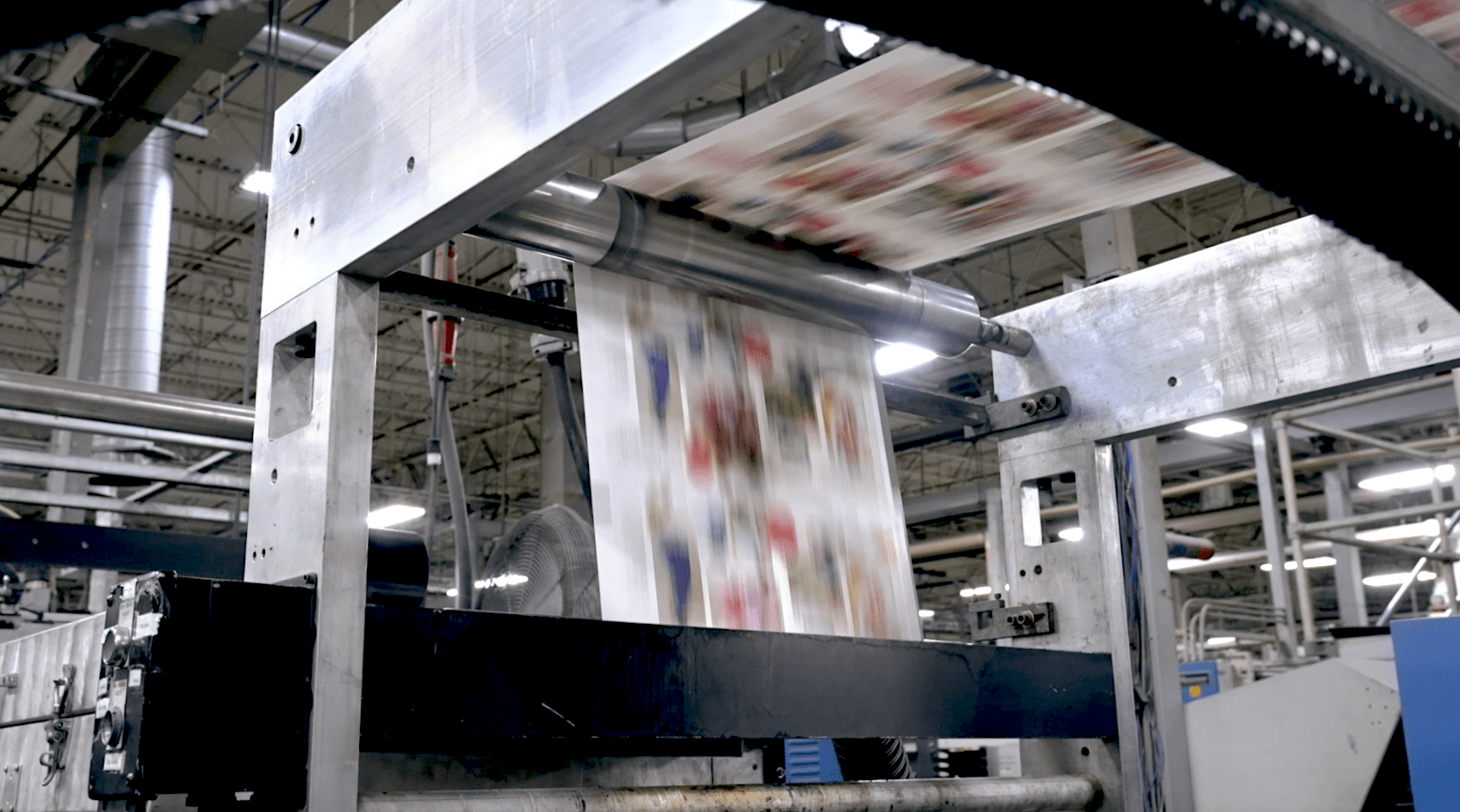

Offset and digital printing are the two most prominent printing methods for design projects. The differences between them are wide-ranging, from flexibility and waste to the cost ratio of longer or shorter production runs.
Though traditional offset printing and digital printing are beneficial methods, each has advantages and disadvantages. Choosing the better printing process will ultimately depend on your project’s specific needs. And with hybrid printing, there is no reason to choose offset over digital.
What is Offset Printing?
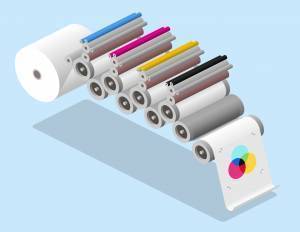
Offset printing requires a plate for each color printed.
Traditional offset printing is a print method that uses aluminum plates to transfer ink onto a rubber sheet (often referred to as a “blanket”). The image is then rolled onto the printing surface. This printing method is considered “offset” because the ink is not transferred to the paper directly.
This method is generally considered the best option when printing large quantities. Although the equipment’s set-up costs are high initially, additional units become relatively less expensive as the quantity increases.
Offset printing allows for a wide range of print materials to be used during production.
It allows the printer to use different paper types, custom finishes, and various inks. The high-quality images produced through offset printing make it the preferred method, especially among graphic designers, when seeking the greatest color reproduction, detail, and professional-looking prints.
Some confusion arises with the idea of “digital offset printing,” which refers to integrating digital technology into traditional offset printing processes, enhancing efficiency and reducing setup times while retaining the fundamental characteristics of offset printing, such as high-quality color reproduction and versatility in print materials. The fundamental printing method remains offset.
What is Digital Inkjet Printing?
For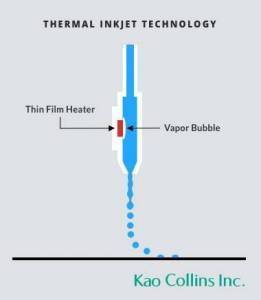 digital inkjet printing, ink is transferred directly onto the surface. Rather than relying on aluminum plates and rubber blankets to transfer an image, digital printing uses liquid ink during production. Traditional home inkjet printers are one of the most common digital printing methods.
digital inkjet printing, ink is transferred directly onto the surface. Rather than relying on aluminum plates and rubber blankets to transfer an image, digital printing uses liquid ink during production. Traditional home inkjet printers are one of the most common digital printing methods.
Digital printing requires no manual setup. It’s highly effective for smaller quantity runs and far more cost-effective than offset printing for low-volume projects.
Because of the lack of setup, digital printing is also a quick process, capable of completing projects on short notice or finishing a job to meet tight deadlines. Digital printing also offers maximum customization. Each piece can be customized, making this method extremely effective if a job needs personalized customer names.
Benefits of Offset Printing
- Better color fidelity refers to both the accuracy of the colors and their balance in the design. Because offset printing can mix custom color inks for each job, it will naturally get the colors spot-on.
- Works equally well on almost any kind of material.
- Reliable, superior image quality. Count on offset printing for clean, distinct types and images without streaks or spots.
- For large-volume jobs, you get more for your money. It costs a lot to start an offset job. You have to invest money into creating the plates, which takes time. However, once you’ve invested it, all of the materials are ready to go, and you’ll spend less on big offset jobs than a digital print, which is about the same per piece no matter how big the job gets.
Benefits of Digital Printing
Contact Kao Collins about Industrial Inkjet Printing
Contact- Unlike offset printing, digital printing offers a fast turnaround time.
- Each print is identical. You risk fewer odd variations caused by imbalances in water and ink.
- Digital printing is less costly for low-volume jobs. The price per unit drops for digital printing, so at some point, they crisscross.
- Changing information within a single print job. For example, say you were printing out postcards advertising a concert. You could change the dates and locations for part of the batch to create two sets of cards for two shows.
Why Convert to Digital Printing from Offset?
While digital printing or inkjet printing is the preferred choice in the present times, there are compelling reasons to convert from offset to digital printing systems.
Color matching
Contact Kao Collins about color matching and custom formulations.
ContactWhen printing offset or digitally, critical decisions and processes are involved in color matching. If it has a graphic overlay or includes a label, it will have colors. It may be as simple as black text on a white background or as complicated as 10 colors. Whichever the case, the color will need to be matched. Color matching of digital printer ink is no longer challenging with dyes and pigments.
Versatility

Industrial inkjet printing offers versatility for printing on many different substrates.
Digital printing is ideal for customers who do not require longer runs and warehousing materials.
- With ever-changing trends comes product variations, and digital printing offers the most cost-effective solution when testing marketing campaigns and limited releases. Smaller-scale product manufacturing creates more demand, and customers tend to buy them before stocks run dry. Under such circumstances, printing, labels, packaging, signage, and promotion can be printed quickly and cost-effectively through digital printing.
- Digital printing also supports just-in-time delivery, eliminating the need to carry inventory, which requires valuable space and time.
- On-demand printing also avoids needlessly creating waste when priorities and designs change.
Handling Errors
Quite often, errors in printing are unavoidable under certain circumstances. This becomes critical in long-run print orders. Fixing mistakes is a tedious exercise and almost impossible in offset printing. However errors like
Misspellings, omissions, corrections, etc., can be easily rectified with digital printing.
Customization and Personalization
Single-unit customization or personalization is one of the biggest demands in modern-day printing. Digital printing’s greatest advantage is the value of personalized services or special customization based on each client’s requirements.
More Choice of Substrates
One advantage of digital printing is choosing from a wide range of digital substrates. With offset printing, substrates make up, on average, 30% of the cost of the job. With digital printing, the cost of the substrate in the overall job is minuscule. This allows for more choices than ever before, and that’s good for marketers and businesses.
Equipment cost
Of the three types of inkjet technology, thermal inkjet (TIJ) offers the lowest cost of entry and cost of ownership. Piezo drop-on-demand is the second printing technology to consider. Continuous inkjet (CIJ) systems require significant maintenance, more operator training, and higher downtime. However, equipment costs in inkjet printing are far lower than offset printing as there are no plate-making, plates, and press expenses. Beyond the capital expense, the prepress equipment and printing presses require highly skilled operators in offset printing, which adds labor costs.
Hybrid Printing Combines Offset and Digital
Hybrid industrial printing systems integrate offset printing with inkjet technology, streamlining the production process on a single-pass line optimized for offset printing. This innovative setup maximizes the advantages of both analog and digital printing methodologies.
Benefits of Adding Digital Printing to Offset Printing Systems
- Enhanced Customization: Digital printing allows for variable data printing, enabling personalized content and designs tailored to individual products or customers.
- Improved Efficiency: Inline digital printing minimizes setup time and reduces waste compared to traditional analog methods, leading to faster turnaround times and cost savings.
- Superior Quality: The combination of offset printing’s high-quality color reproduction and digital printing’s precision results in sharp, vibrant graphics and text.
- Versatility: Hybrid systems can handle various substrates and applications, from labels and packaging to security and pharmaceutical products.
- Sustainable Practices: Digital printing consumes fewer resources and generates less waste, contributing to eco-friendly printing practices and reduced environmental impact.
Common Applications for Hybrid Offset-Digital Printing Systems
- Household, personal care, food, and beverage labels
- Security and pharmaceutical labels requiring variable data or unique identifiers
- Automotive and retail product labels with intricate designs and branding elements
- Flexible packaging for various consumer goods
- Laminate tubes and shrink sleeves
By integrating digital solutions into offset printing, hybrid industrial printing systems offer a versatile and efficient solution for diverse printing needs while maintaining the high standards of quality and customization required by modern industries.
The Kao Collins X-BAR print module integrates digital inkjet capabilities with inline offset printing systems, enhancing versatility, efficiency, and quality. Its features include integrating existing equipment, improved productivity, high-quality output, and cost-effectiveness. Typical applications include labels, packaging, security labels, automotive, retail, and specialty products like laminate tubes and shrink sleeves.
X-BAR Benefits
- High throughput and maximum uptime for improved productivity
- Premium quality output with sharp and clear results
- Needed flexibility with advanced inks for substrate compatibility
- Significant savings on consumables leading to accelerated ROI
- Fast restarts, zero charge shorts, and zero streakers to reduce downtime
- Future-proof production with the Kao Collins Universal Controller
- Higher DPI (1,200 dpi at 1,000 fpm) for superior print quality
Comparing Industrial Inkjet and Offset Printing
| Benefit | Offset | Industrial Inkjet |
| Quickest turnaround | ✓ | |
| Cost-effectiveness for shorter runs | ✓ | |
| Cost-effectiveness for longer runs | ✓ | |
| Most accurate color matching | ✓ | |
| Substrate compatibility | ✓ | |
| Ease of proofing | ✓ | |
| Mass customization | ✓ | |
| Cost of ownership | ✓ |
Frequently Asked Questions
Digital printing technology transfers images directly from digital files to substrates without using plates, making it faster and cheaper for short runs. It supports personalized printing, offers high-quality results and quick turnaround times, and works on diverse materials like metal, plastics, cardboard, and fabric. It also reduces waste and lowers ink and chemical usage, making it more sustainable and eco-friendly.
What does “Digital Offset Printing” mean?
Digital offset printing refers to highly automated offset printers that streamline setup and changeover processes, although the fundamental printing method remains offset.
No, offset printing is not suitable for variable data printing, which is an exclusive capability of digital printing methods.
Digital printing transfers color directly to the paper, while offset printing uses separate plates for each color component, transferring ink to a blanket cylinder before printing.
Industrial inkjet printing offers quicker turnaround times, cost-effectiveness for shorter runs, more accurate color matching, substrate compatibility, ease of proofing, mass customization, and lower cost of ownership.
These systems are used for labels, packaging, addressing transactional documents, flexible packaging, security labels, and shrink sleeves.
Offset printing uses aluminum plates and rubber sheets to transfer ink onto paper, while inkjet printing directly transfers liquid ink onto the surface.
The X-BAR print module integrates digital inkjet capabilities with inline offset printing systems, providing high throughput, premium quality output, substrate flexibility, cost savings, and future-proof production.






